线段树
大约 3 分钟
线段树
在计算机科学中,线段树(Segment Tree)也被称为统计树,用于存储有关区间或段的信息。它允许查询存储的段中是否包含给定点。从原理上讲,它是一种静态结构,即一旦构建,就无法修改的结构。类似的数据结构是区间树(Interval Tree)。
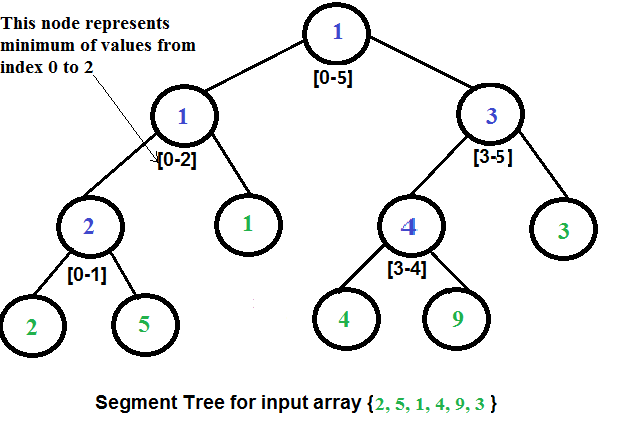
线段树是一棵二叉树。树的根节点表示整个数组。根节点的两个子节点分别表示数组的前半部分和后半部分。同样,每个节点的子节点对应于与节点相对应的数组的两个部分。
我们自底向上构建树,每个节点的值是其子节点值的“最小值”(或任何其他函数)。这将花费 O(n log n) 的时间。所做的操作次数是树的高度,即 O(log n)。要进行范围查询,每个节点将查询分成两个部分,即每个子节点的子查询。如果查询包含节点的整个子数组,我们可以使用节点上预计算的值。使用这种优化,我们可以证明只执行 O(log n) 个最小值操作。

应用
线段树是一种旨在高效执行某些数组操作的数据结构,特别是涉及范围查询的操作。
线段树的应用领域包括计算几何和地理信息系统。
线段树的当前实现意味着您可以向其传递任何二元(带有两个输入参数)函数,从而可以对各种函数进行范围查询。在测试中,您可以找到对线段树进行最小值、最大值和求和范围查询的示例。
完整代码
import isPowerOfTwo from '../../../algorithms/math/is-power-of-two/isPowerOfTwo';
export default class SegmentTree {
/**
* @param {number[]} inputArray
* @param {function} operation - binary function (i.e. sum, min)
* @param {number} operationFallback - operation fallback value (i.e. 0 for sum, Infinity for min)
*/
constructor(inputArray, operation, operationFallback) {
this.inputArray = inputArray;
this.operation = operation;
this.operationFallback = operationFallback;
// Init array representation of segment tree.
this.segmentTree = this.initSegmentTree(this.inputArray);
this.buildSegmentTree();
}
/**
* @param {number[]} inputArray
* @return {number[]}
*/
initSegmentTree(inputArray) {
let segmentTreeArrayLength;
const inputArrayLength = inputArray.length;
if (isPowerOfTwo(inputArrayLength)) {
// If original array length is a power of two.
segmentTreeArrayLength = (2 * inputArrayLength) - 1;
} else {
// If original array length is not a power of two then we need to find
// next number that is a power of two and use it to calculate
// tree array size. This is happens because we need to fill empty children
// in perfect binary tree with nulls.And those nulls need extra space.
const currentPower = Math.floor(Math.log2(inputArrayLength));
const nextPower = currentPower + 1;
const nextPowerOfTwoNumber = 2 ** nextPower;
segmentTreeArrayLength = (2 * nextPowerOfTwoNumber) - 1;
}
return new Array(segmentTreeArrayLength).fill(null);
}
/**
* Build segment tree.
*/
buildSegmentTree() {
const leftIndex = 0;
const rightIndex = this.inputArray.length - 1;
const position = 0;
this.buildTreeRecursively(leftIndex, rightIndex, position);
}
/**
* Build segment tree recursively.
*
* @param {number} leftInputIndex
* @param {number} rightInputIndex
* @param {number} position
*/
buildTreeRecursively(leftInputIndex, rightInputIndex, position) {
// If low input index and high input index are equal that would mean
// the we have finished splitting and we are already came to the leaf
// of the segment tree. We need to copy this leaf value from input
// array to segment tree.
if (leftInputIndex === rightInputIndex) {
this.segmentTree[position] = this.inputArray[leftInputIndex];
return;
}
// Split input array on two halves and process them recursively.
const middleIndex = Math.floor((leftInputIndex + rightInputIndex) / 2);
// Process left half of the input array.
this.buildTreeRecursively(leftInputIndex, middleIndex, this.getLeftChildIndex(position));
// Process right half of the input array.
this.buildTreeRecursively(middleIndex + 1, rightInputIndex, this.getRightChildIndex(position));
// Once every tree leaf is not empty we're able to build tree bottom up using
// provided operation function.
this.segmentTree[position] = this.operation(
this.segmentTree[this.getLeftChildIndex(position)],
this.segmentTree[this.getRightChildIndex(position)],
);
}
/**
* Do range query on segment tree in context of this.operation function.
*
* @param {number} queryLeftIndex
* @param {number} queryRightIndex
* @return {number}
*/
rangeQuery(queryLeftIndex, queryRightIndex) {
const leftIndex = 0;
const rightIndex = this.inputArray.length - 1;
const position = 0;
return this.rangeQueryRecursive(
queryLeftIndex,
queryRightIndex,
leftIndex,
rightIndex,
position,
);
}
/**
* Do range query on segment tree recursively in context of this.operation function.
*
* @param {number} queryLeftIndex - left index of the query
* @param {number} queryRightIndex - right index of the query
* @param {number} leftIndex - left index of input array segment
* @param {number} rightIndex - right index of input array segment
* @param {number} position - root position in binary tree
* @return {number}
*/
rangeQueryRecursive(queryLeftIndex, queryRightIndex, leftIndex, rightIndex, position) {
if (queryLeftIndex <= leftIndex && queryRightIndex >= rightIndex) {
// Total overlap.
return this.segmentTree[position];
}
if (queryLeftIndex > rightIndex || queryRightIndex < leftIndex) {
// No overlap.
return this.operationFallback;
}
// Partial overlap.
const middleIndex = Math.floor((leftIndex + rightIndex) / 2);
const leftOperationResult = this.rangeQueryRecursive(
queryLeftIndex,
queryRightIndex,
leftIndex,
middleIndex,
this.getLeftChildIndex(position),
);
const rightOperationResult = this.rangeQueryRecursive(
queryLeftIndex,
queryRightIndex,
middleIndex + 1,
rightIndex,
this.getRightChildIndex(position),
);
return this.operation(leftOperationResult, rightOperationResult);
}
/**
* Left child index.
* @param {number} parentIndex
* @return {number}
*/
getLeftChildIndex(parentIndex) {
return (2 * parentIndex) + 1;
}
/**
* Right child index.
* @param {number} parentIndex
* @return {number}
*/
getRightChildIndex(parentIndex) {
return (2 * parentIndex) + 2;
}
}