广度优先搜索(BFS)
大约 1 分钟
广度优先搜索(BFS)
广度优先搜索(BFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图数据结构的算法。它从树根(或图中的任意节点,有时称为“搜索键”)开始,首先探索邻居节点,然后再移动到下一层的邻居节点。
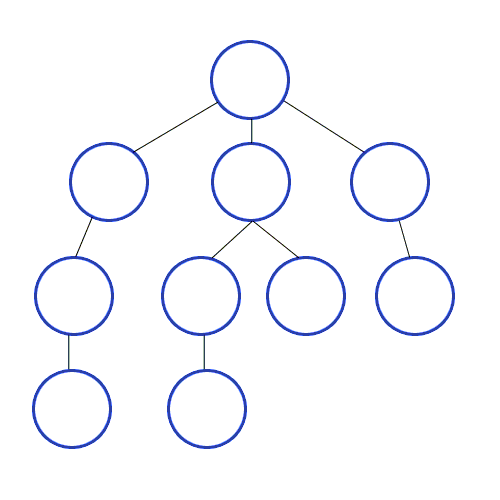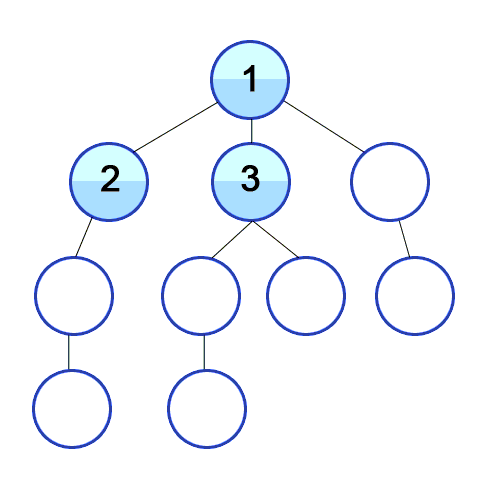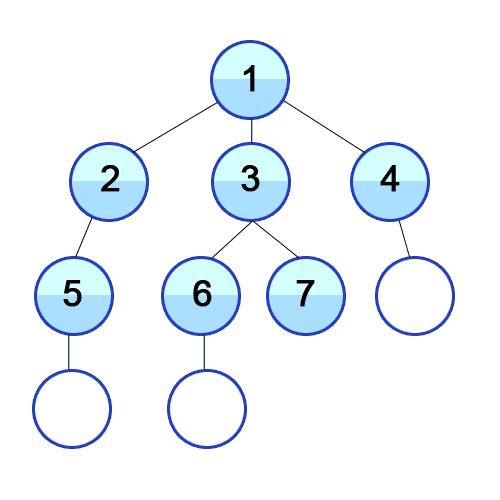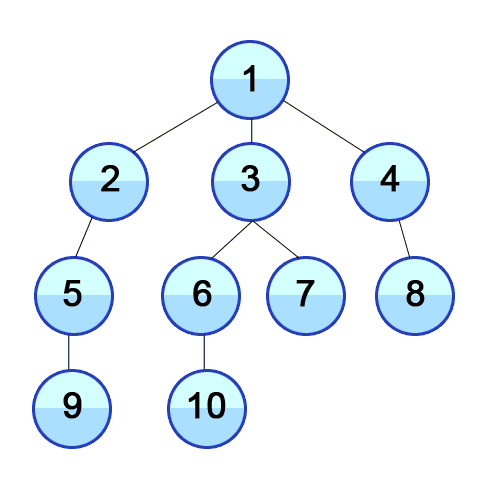
伪代码
BFS(root)
Pre: root is the node of the BST
Post: the nodes in the BST have been visited in breadth first order
q ← queue
while root = ø
yield root.value
if root.left = ø
q.enqueue(root.left)
end if
if root.right = ø
q.enqueue(root.right)
end if
if !q.isEmpty()
root ← q.dequeue()
else
root ← ø
end if
end while
end BFS
完整实现
import Queue from '../../../data-structures/queue/Queue';
/**
* @typedef {Object} Callbacks
* @property {function(node: BinaryTreeNode, child: BinaryTreeNode): boolean} allowTraversal -
* Determines whether BFS should traverse from the node to its child.
* @property {function(node: BinaryTreeNode)} enterNode - Called when BFS enters the node.
* @property {function(node: BinaryTreeNode)} leaveNode - Called when BFS leaves the node.
*/
/**
* @param {Callbacks} [callbacks]
* @returns {Callbacks}
*/
function initCallbacks(callbacks = {}) {
const initiatedCallback = callbacks;
const stubCallback = () => {};
const defaultAllowTraversal = () => true;
initiatedCallback.allowTraversal = callbacks.allowTraversal || defaultAllowTraversal;
initiatedCallback.enterNode = callbacks.enterNode || stubCallback;
initiatedCallback.leaveNode = callbacks.leaveNode || stubCallback;
return initiatedCallback;
}
/**
* @param {BinaryTreeNode} rootNode
* @param {Callbacks} [originalCallbacks]
*/
export default function breadthFirstSearch(rootNode, originalCallbacks) {
const callbacks = initCallbacks(originalCallbacks);
const nodeQueue = new Queue();
// Do initial queue setup.
nodeQueue.enqueue(rootNode);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
const currentNode = nodeQueue.dequeue();
callbacks.enterNode(currentNode);
// Add all children to the queue for future traversals.
// Traverse left branch.
if (currentNode.left && callbacks.allowTraversal(currentNode, currentNode.left)) {
nodeQueue.enqueue(currentNode.left);
}
// Traverse right branch.
if (currentNode.right && callbacks.allowTraversal(currentNode, currentNode.right)) {
nodeQueue.enqueue(currentNode.right);
}
callbacks.leaveNode(currentNode);
}
}